
Mapping the challenges of Node.js applications has never been easier, especially in the production environment.
Node.js application holds numerous major elements, such as memory utilization, memory leaks, and the deployment process, making its monitoring critical.
Monitoring is the process of tracking a software’s quality over time. Application Performance Monitoring, or APM, is the name used to describe the products and tools offered in this market.
Node.js applications can be monitored on multiple levels in a staging or production environment.
You can keep an eye on things like:
- Individual servers
- Regions
- Zones,
- and the Node.js software that runs on them
But in this blog, we’ll only cover the software components,
Every production in a software development system requires application monitoring. And it can be accomplished in a variety of ways, from basic health checks to more complicated setups in which a monitoring library is embedded into your server and feeds data to a dedicated monitoring service. It can also incorporate the client-side of your software, providing additional in-depth information about the user experience.
Monitoring is an important element of every development process since you need to know how the software acts in production.
Tip – You can give your testers access to your system and have them try to simulate interactions or high loads.
But, first, we need to know what should be monitored.
Each Node.js application generates a large amount of data in its operation. In order to monitor Node.js applications, a developer or a tester needs to consider the following levels
- Service level
- Host level
- Process level
A good APM should be able to provide insights on the above aspects. This post will teach you how to use PM2 to monitor your Nodejs application correctly.
What is PM2?
PM2 is an open-source, advanced, and effective production process manager for Node. JS-based apps. PM2 is used to operate and monitor live production workloads using a CLI or web interface.
A load balancer is incorporated into the PM2. It enables the application to be monitored. It allows the user to refresh the program without disrupting the service. It facilitates system admin duties and allows auto-restart with effective management of apps, services, and processes. It has tools for hardening your existing PM2 as well as monitoring apps in production across several servers.

PM2 is compatible with NodeJS-based web application frameworks such as Express, Hapi, Geddy, and Sail.
What are the key Features of PM2?
- It allows the application to be executed continuously without any interruption
- PM2 manages all processes Such as start, stop, restart, delete, show and monitor
- It allows auto-start and auto-shutdown
- Web interface integration for monitoring application health and metrics
- Log streaming to a web interface
- Maximum memory reload without downtime
- Performance metrics can be seen on the application
- Built-in Load Balancer
- Process Monitoring
- It makes the applications run as a service.
- It makes the applications secure by not running the service as root.
- It maintains the log of each and every exception

Getting Started with PM2
Make sure you have NPM installed before installing PM2. Use the command below to verify NPM’s installation and version.
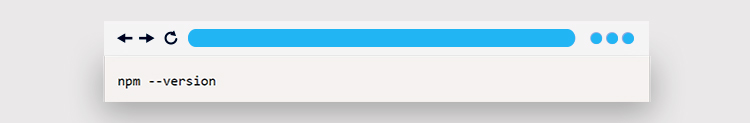
If NPM is installed, this command should display its version. Additionally, run the following command to install PM2:
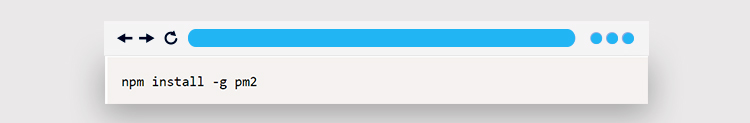
The -g (global flag) option installs the module and makes it available as a command globally. To begin using PM2, navigate to the folder containing the NodeJS project and run the command below:
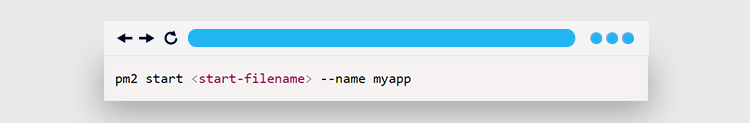
The command above starts a NodeJs application with the file supplied in the first argument as its input. The application is also given the moniker my app. When using pm2 to run a NodeJS application, it ensures that the service does not go down, and if it does, it attempts to restart the application automatically.
What are the steps for the Usage of PM2?
Start :
PM2 has the most basic command for starting, daemonizing, and monitoring your program.
start helloworld.js in pm2
The command below can be used to change the name of your process.
helloworld.js -name pm2 start MyWorld
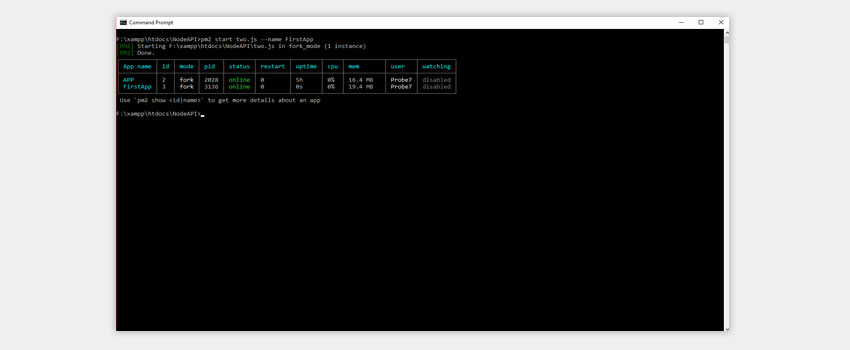
List:
Use the below-written command and get all the processes displayed with status
pm2 list
Stop:
To stop an application, you can use the below command.
pm2 stop <id|name>
//Stop all processes
pm2 stop all
Restart:
Restart the previously launched app by
pm2 restart <id|name>
pm2 restart all
Delete:
stop and delete a process from the pm2 process list
pm2 delete <id|name> pm2 delete all
Details:
To get more details about an application
pm2 show <id|name>
Monitor:
You can monitor the resource usage of your application with :
pm2 monit pm2 Monit <id|name>
Kill:
To stop the PM2
pm2 kill
Logs:
Your application logs will be stored on the server hard disk.
pm2 logs
What are the Best Practices of PM2?
Scale any application with PM2 seamlessly with little to no errors
- One codebase tracked in revision control, many deploys
- Explicitly declare and isolate dependencies
- Store configuration in the environment
- Treat backing services as attached resources
- Strictly separate build and run stages
- Execute the app as one or more stateless processes
- Export services via port binding
- Scale-out via the process model
- Maximize robustness with fast startup and graceful shutdown
- Keep development, staging, and production as similar as possible
- Treat logs as event streams
- Run admin/management tasks as one-off processes
Final Thoughts
Maintaining your codebase and keeping it relevant is challenging, but keeping an application alive and operating is even more difficult. Because most of our backend APIs are written in Node.js, scaling a single-threaded process can be challenging; this is where PM2 comes in. There are numerous process managers available, including Forever, StrongLoop’s Process Manager, and good old SystemD. We chose PM2 at Brainvire because it is simple to use and makes managing a production environment a breeze. Contact us to check out our Node.js development services.
Related Articles
-
Reasons to Be Addicted to Node.js for Real-Time Application Development
In a society where everything moves so fast- especially technology that becomes obsolete much quicker than we would like to admit- there has been an endless search to create more
-
Why Should You Use Node.js for Your Application
Talking About Why Should You Use Node.js for Your Application, Waiting for your order on the same counter at which you have ordered is annoying for both you and the
-
What is NodeJS and Why You Should Use It For Enterprise Apps?
The sky-high popularity of JavaScript is changing the face of web development drastically. The things we are able to do on the web nowadays are truly incredible, and one of




