Let’s admit this. You might be a jack of all trades but achieving customer satisfaction is not at all a piece of cake. It’s such a herculean task where you would leave no stone unturned to accomplish it, but it could still go in vain. However, the immense technological transformation significantly helped many businesses to grow and sustain their competencies.
Being one of the most revolutionary inventions, the Internet can aid industries to grow their trade to reap huge returns.
Let’s Understand IoT
IoT, in general, links together the devices for the specialized function with limited or restricted customization or programmability. It can be considered the cyber-physical system since it derives the data from the physical world through its dynamic sensors. Well, let’s get this through the simple examples given below.
- These days, it’s easy to come across a lightbulb which can be operated through your smartphone. Well, this element is part of the IoT.
- It was never that easy to monitor your calories or heartbeat through wearable devices.
- It’s common to witness smart homes that comprise smart devices to enhance their security.
- Your smartwatch helps you to manage your smartphone. Well, let’s clap for IoT.
IoT involves the devices which can communicate or share the data not always through the internet but not always relying upon any sort of human involvement. Thus, your PC or Smartphone can’t always be called IoT, but your smartwatch or fitness band surely belongs to IoT.
IoT in Manufacturing (Industrial Internet of Things)
IoT is the industrial internet of things. It is a network of physical objects that collects data with the help of sensors and interacts with the physical world.
The industrial internet of things provides you with insights into how your assets are performing in real-time.
IIoT comprises tremendous digital transformation in manufacturing that utilizes the web of various sensors to gather crucial data and uses Cloud software to turn this data into conclusive insights about the efficiency of the manufacturing operations.
IIoT applications can significantly improve efficiency and productivity by optimizing operations, production, logistics, and service delivery processes. It can also help troubleshoot problems in equipment, assembly line, production line, or any other industrial setup you may have.
The manufacturing industries can’t resist implementing IoT phenomena because of the growing demand and supply chain across the globe. Several manufacturing industries have already witnessed immense outcomes as IoT integrated their productivity and widened their market.
DID YOU KNOW?
The assembly line at Toyota Motor Manufacturing in Kentucky can connect all factory equipment, vehicles, and even workers to the network. This allows the company to gather data from all devices that are installed on the network. All of this data is then analyzed by a machine that produces reports about energy use, production times, and areas for improvement.
Major Factors Leading to IIoT Adoption in Manufacturing Sector
- Cost Reduction: Thanks to its asset optimization and enhanced management of inventories, it greatly reduces the cost incurred for inventory carriage and search time. Now, a company can save huge in terms of its operational expenses and generate a huge rate of returns instead. In addition, products with smart elements enable you to shift from selling a product to selling an experience. This yields efficiency in post-sale service.
- Shorter-Time-to-Market: It is laced with faster and more efficient manufacturing supply chain operations that reduce the product cycle time. Let’s take an example of Harley Davidson that considered leveraging the IoT phenomena to reconfigure its York, PA manufacturing facility and significantly reduced the time to make its motorbike from 21 to 6 days.
- Mass Customization: It indeed takes a dramatic increase in the variety of produced stock-keeping units to expand the inventory. This makes the manufacturing process quite complex too.
The production of several stock-keeping units occurs, making it an arduous task to track the inventory operations. Well, IIoT provides mass customization by becoming a prime source of real-time data that is essential for thoughtful processing, shop floor scheduling, and routing.
- Improved Safety: IIoT ensures a safer workplace due to the wearable devices which efficiently monitor workers’ health status and their activities which can cause damage. Besides this, IIoT denotes a serious issue even in hazardous environments.
The oil and gas industry, for instance, utilizes IIoT to detect issues like gas leakage as it is linked to the pipe network. Isn’t it interesting?
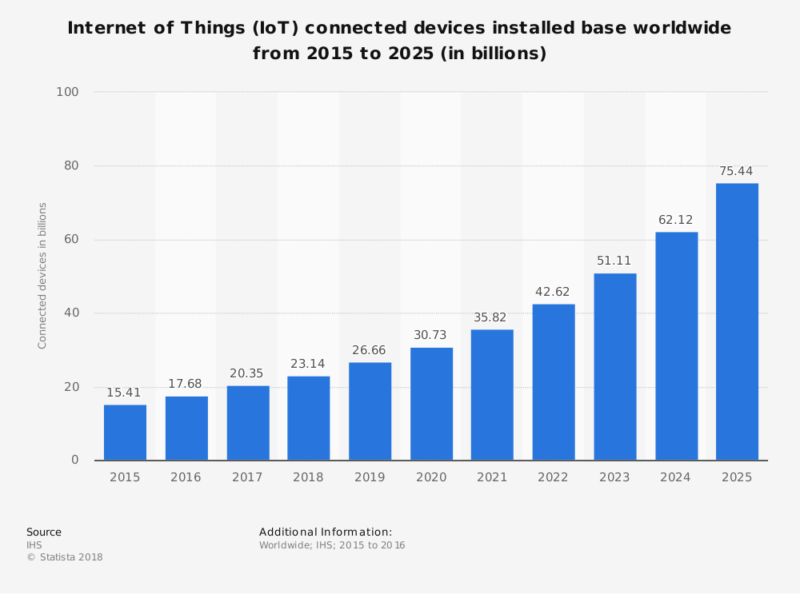
IIoT Adoption with Statistics
| As per the reports of CGI,62 % of manufacturing enterprises implemented digital transformation pilots and programs. |
| BSquare Annual maturity Report states that 86% of manufacturers already adopted IIoT based solutions, and 84% of them found it effective. |
| As per the estimation by McKinsey, the IIoT application has the potential to generate $1.2 to 3.7 trillion economic value by 2025. |
IIoT Impact and its Three Major Dimensions
It can’t be denied that the IoT-based solutions transformed the production and its ways of operation. It has brought major improvement across three dimensions.
Dimension 1: Enabling Visibility from Top Floor to Shop Floor and Field Operations
The phenomenal IIoT provides supervision to shop floors and field operations along with possible control over resources. The lead solutions like ERP and MES failed to bridge the gap that IoT technology filled. It helped mitigate the reliance on manual data inputs and the inability to handle meticulous reports such as real-time records of equipment and inventory items.
The industries could significantly boost their productivity as IIoT provides detailed shop floor data. There are two major categories under which the IIoT solutions enable the manufacturers to attain a significant level of shop visibility.
- Applications for Manufacturing Operations: As per McKinsey’s estimation, the IoT-driven operations with tremendous transformation would incur more than $420 Billion per year.
| IoT solutions to track machine utilization can boost manufacturing productivity by 10 to 25% and generate a $1.8 trillion global economy by 2025. -ITFI Research |
Tracking real-time machine utilization via IoT applications can yield accurate utilization metrics. It offers meticulous reports of what is happening at each stage of the production.
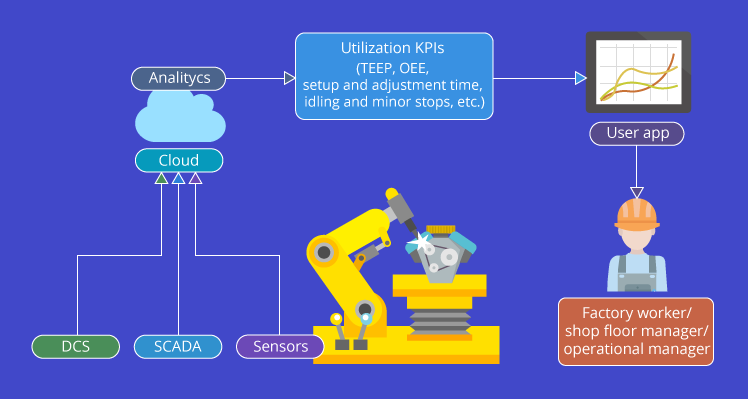
There are two ways to perform the quality check on the produced goods. One is by analyzing work in progress status as it thoroughly studies the production cycle by supervising the calibration of the machine through which the product is manufactured. This process yields more accurate results as it helps in finding minor defects. However, it has some drawbacks.
- Only in the case of distinct manufacturing; the WIP (Work in Progress) based quality supervision is considerable
- It consumes time, labor, and money as it is done manually
- Supervising each and every WIPs is not always feasible. And thus, it presents a fractional view in terms of quality supervision
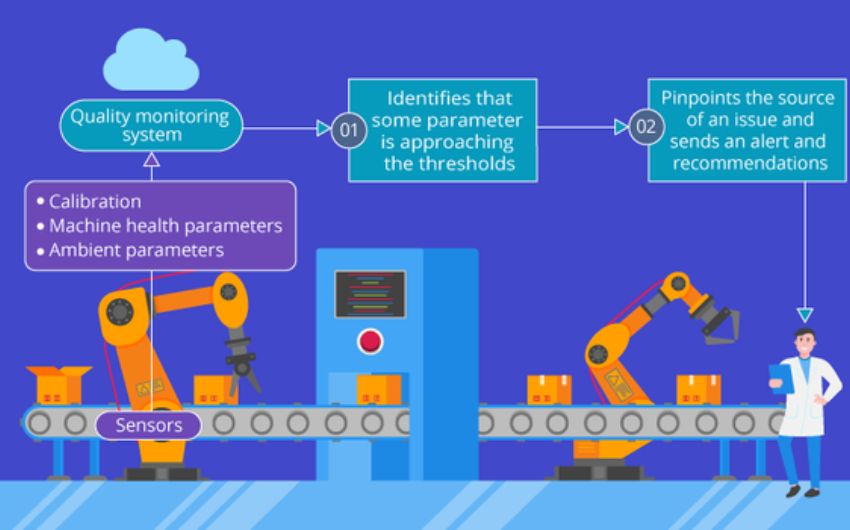
The second method comprises monitoring the condition and calibration of a machine. It gives less differentiation in the case of scope. It upholds simple binary categorization; good and not good. This method effectively tracks the bottleneck in manufacturing, identifies underperforming assets, and timely provides machine damage.
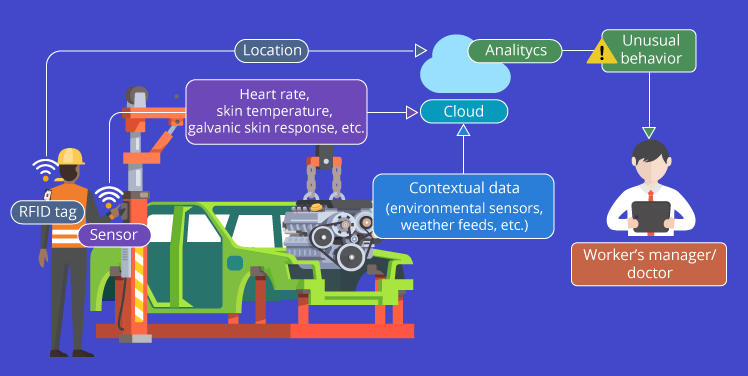
- Applications for Industrial Asset Management: The IoT solutions are considered in manufacturing to ensure proper asset usage, boost the equipment service life and improve reliability to get the best from the assets. There are three parameters through which the IoT enables asset management, including industrial asset tracking, inventory management, and predictive maintenance through monitoring conditions.
Dimension 2: Enabling Visibility across the Manufacturing Supply Chain
An end-to-end supply chain for 52% of the manufacturers is still a challenge. Although, IoT-based supply chain monitoring has optimized this process. The manufacturers can track the real-time insights regarding the location, status, and condition of every object with the help of smart supply chain solutions.
On the contrary, a manufacturer would only have access to only general data of SKUs in traditional supply chain solutions. The IoT is also utilized for the purpose of monitoring the conditions under which a particular object is brought or stored. This was quite difficult earlier as such conditions could only be supervised once the object reached the delivery point.
It has become simple to track the condition of goods, components, and other materials en route, which is quite crucial for the manufacturers of breakable and perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals, glassware, and food.
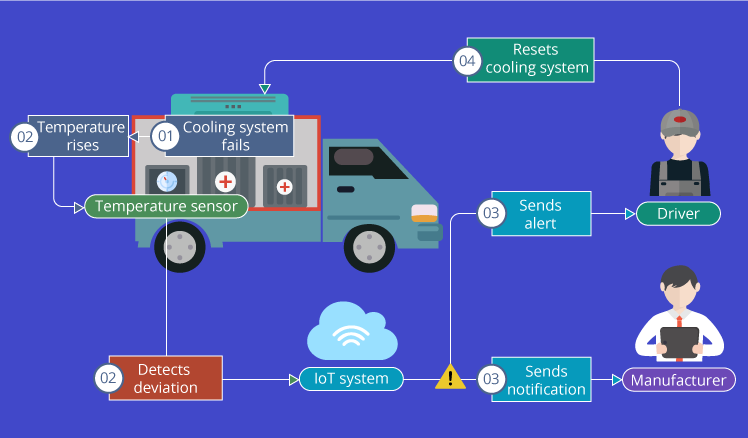
Dimension 3: Enabling Visibility across remote and Outsourced Operations
Demand for the distribution of shop floors is rising because of challenges like high logistic costs, an increase in the global supply chain, and a lack of local talent that leads to relying on outsourcing. Irrespective of where a manufacturer sets up his company, he must maintain its manufacturing and production standards such as material testing, predictive maintenance, and industrial automation.
Besides this, IoT promotes distributed operations through industrial smart and connected products. The complex system of the network comprises sensors, embedded intelligence, hardware, and Cloud software. For example, the smart connected products in Mumbai, India, can be monitored by the enterprise manager in Delhi or New York.
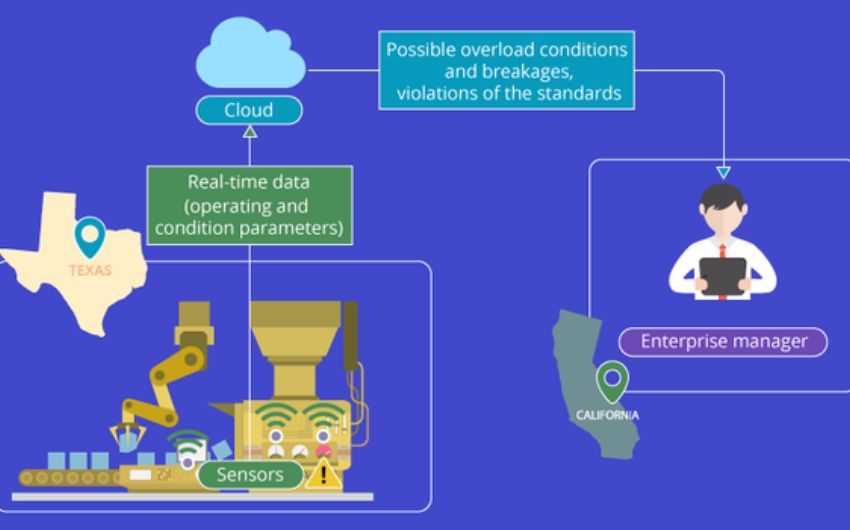
It helps in monitoring conditions like changes in temperature of transponders and severely high rotation speed of milling machine splinters. Through this, managers can know about the violation of standard operating procedures. Well, IoT has a lot to offer, doesn’t it?
IIoT and its Challenges
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is defined as a set of technologies that create a digital link between physical devices and IT systems in the factory. One of the benefits of connecting physical devices to an IT system is that it makes running a production line easier and more efficient. However, the transmission and use of data also have some risks and challenges.
However, it also has some challenges, including huge investment, uncertainty in terms of ROI, lack of qualified operators/employees, the transmission and use of data, and privacy. Its inability to perform fast experiments and absence of IoT standards are some of the parts of concern.
There are two main areas where IIoT can cause security concerns:
1) Sensitive information such as personal data or intellectual property
2) The control systems for machines such as robots
The problems with power consumption in IIoT systems arise because most machines are battery-powered, which limits their use in their lifetime, and may cause safety hazards or environmental issues if not disposed of correctly or recycled. This can be seen as a problem, as the maintenance and upkeep costs for these machines may rise considering higher power consumption rates, which may further drive up costs.
The Bottom Line
The IIoT solutions significantly help the business to monitor their productivity and supply chain. This is possible because of its asset management mechanism along with operation monitoring. However, the complex nature of industries across the globe demands insightful representation or orchestration throughout every segment of design and execution.
Related Articles
-
Make Healthcare Industry Smarter with Internet of Things
The experts have always tried to enhance the process of treating human health. They put all their efforts to cure patients with new treatments and technology. These things are developed
-
IoT in Retail POS: Past, Present, and Future
You enter a store looking for a new pair of jeans. Your smartphone pings as you go in, and you open it to see a map indicating where the brand
-
Why Node.js is a Natural Fit for IoT Applications?
Talking About Why Node.js is a Natural Fit for IoT Applications? In order to leverage technology to activate business growth, one has to keep an eye on technological expansion. That



